ML Model Workflow Management
Introducing ML model setup in BMC Edge as a technical enhancement & a strategic enabler to keep BMC as a leader in Operation Management industry.
04
My Role
Lead designer, Strategy alignment, End-to-end UX & interaction design, Design system contribution
05
Team
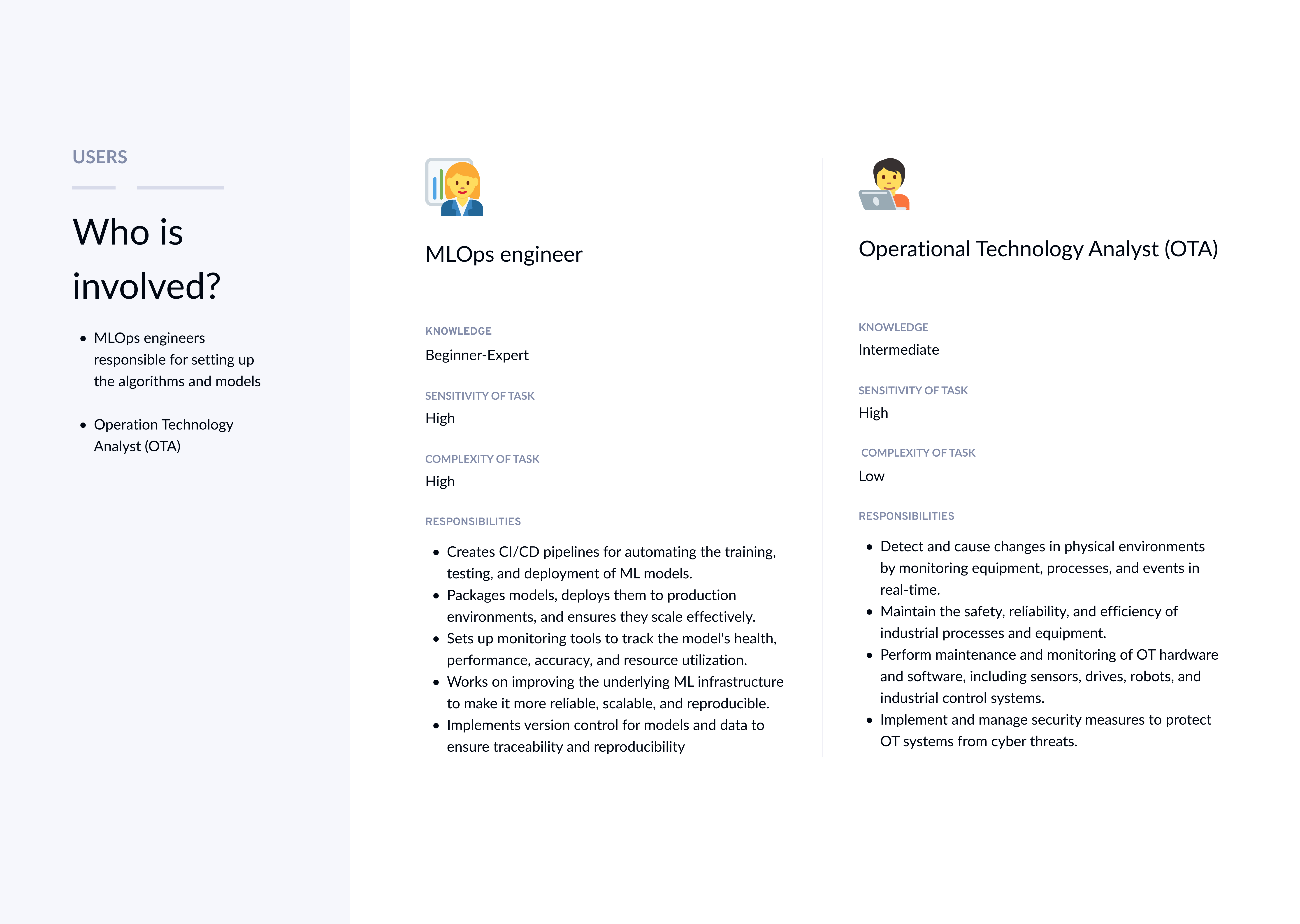
8+ teams: UX Design, Product, Research, Design Systems, Data Science, MLOps, IoT Edge & Branch monitoring, Engineering
06
Lesson
Even highly technical users benefit from layered information design, where complexity is revealed only when needed, reducing cognitive load.
Results & impact
60%
Faster
ML model setup
55% Adoption
Across Edge customer
~20 Minutes
Anomaly model setup
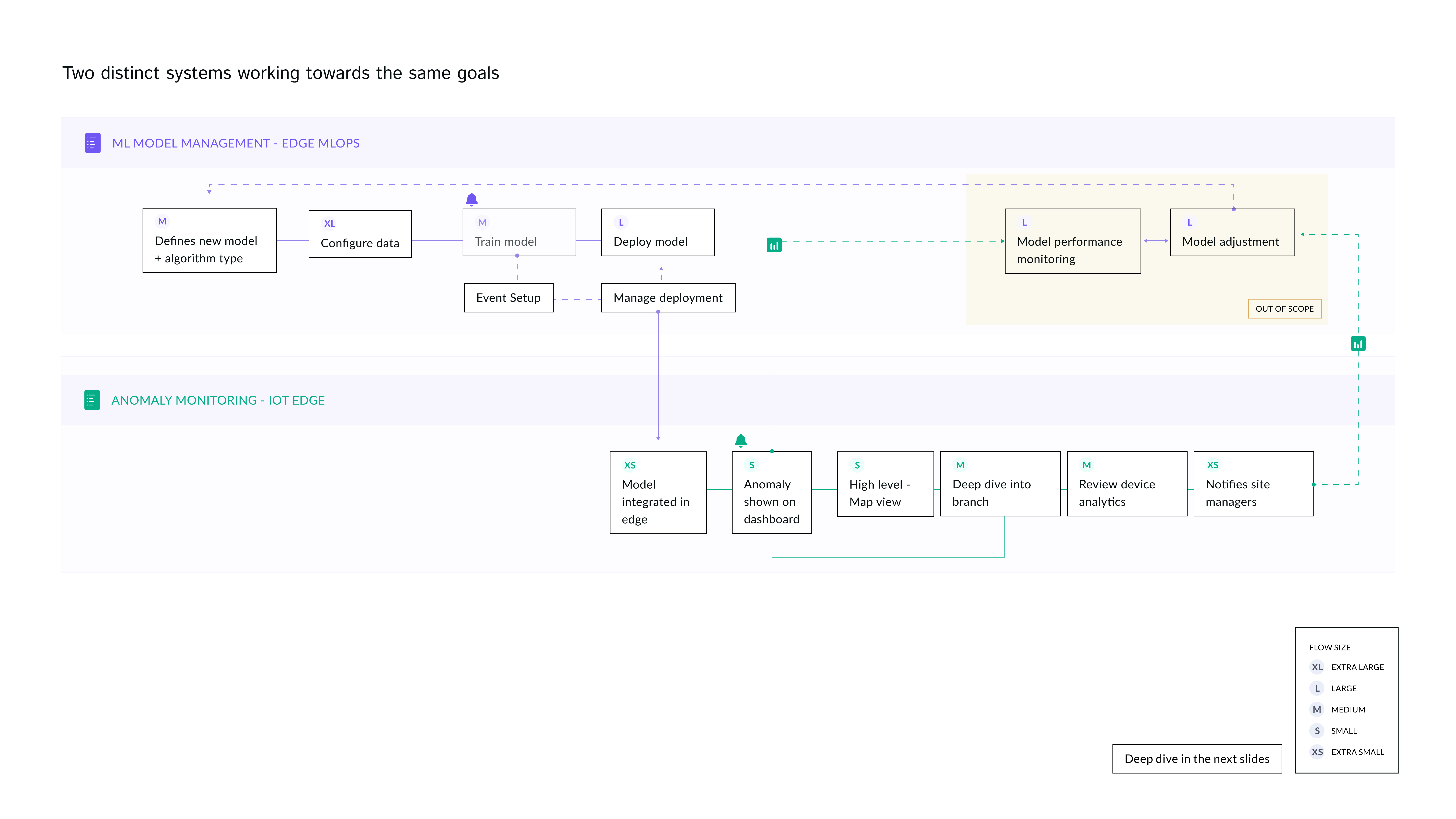
Mapped the detailed process & identified missing features
After customer interviews, I mapped the detailed process including all necessary feature for each step. This informed the design requirements and helped the cross-functional team to better plan for development.

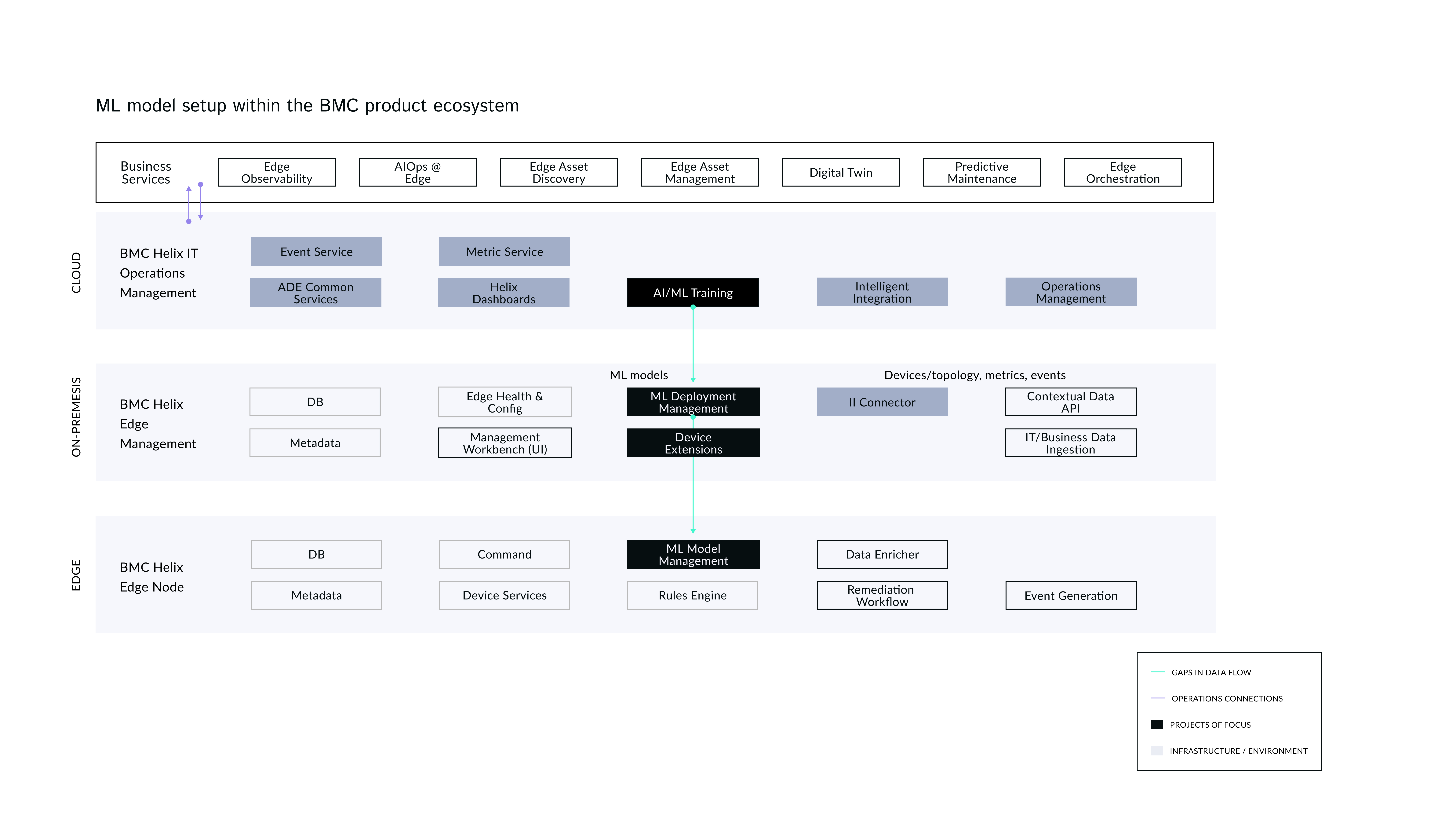
Background
The BMC Edge ML (Machine Learning) Workflow is important because it supports intelligent, real-time decision-making at the edge of enterprise IT environments, especially in complex, distributed, and hybrid infrastructure landscapes.
Why it matters?
Introducing ML workflows in BMC Edge is not just a technical enhancement, it's a strategic enabler to keep BMC as a leader in Operation Management industry.
Identifying the right problem to solve
Step 1: Create new ML model
Process
I broke down the design process into 4 steps and started with low-hanging fruit item which had the least technical dependency. I leveraged existing design pattern for step 1 to ensure alignment with the release deadline.
Navigating resource constraints is a key UX skill. With limited time and budget restricting direct user outreach, I strategically leveraged stakeholders who were also the actual target users. I facilitated workshops to co-create solutions that balanced user needs, business goals, and technical feasibility.
Workflow sequence for creating a new model
1. Name
2. Description
3. Task type
4. Algorithm type (select from existing)
5. Algorithm (select from existing)
6. Framework
Defined where in IoT Edge information architecture

Identified capability gaps for the workflow

Flow exploration
How might we design a simplified ML model lifecycle management enabling technical users to create, train, deploy models to speed up anomaly detection?
01 - Create New Model
Need: New model creation connecting to algorithms
Users needed a clear and intuitive way to start the process of creating a new ML model, ensuring entry point isn't buried and require prior knowledge of where to begin.
Action
Introduced a prominent “New Model” entry point on the ML dashboard followed by connecting to related algorithm.
Impact
More users initiated model builds confidently, and the workflow began with better-prepared inputs, improving downstream success rates.

Step 2: Configuring model
Process
Based on the research and workflow mapping I've done earlier, I ensured design reflects the right sequence for tasks users need to perform.
Through working collaboratively with MLOps experts and iterative testing, we refined the workflow’s usability and uncovered key insights that shaped the direction of our next milestone: Training and deploying models.
Configuration steps:
1. Define device profile
2. Customize data collection intervals
3. Define data filters
4. Collect health scores
02- Configure Input Data
Need: Define 'Device Profile'
Users needed a structured way to define which device types, sensor metrics, and operational behaviors should be included in the model.
Action
Designed a Device Profile definition step where users select device groups, specify metrics, and business attributes. The UI includes presets for common device classes and inline validation to flag missing or incompatible data sources.
Impact
This ensured the ML model was grounded in the specific characteristics of the devices being monitored, improving input consistency and reducing false positives in anomaly detection.

02 - Set Data Collection Rules
Need: Set Data Collection Rules
Users needed a way to define how device data is collected and normalized across distributed edge environments, since inconsistent sampling intervals and unmerged sensor streams led to noisy inputs and unreliable anomaly detection. Without control over these parameters, ML models struggled to reflect real operational behavior.
Action
Added granular data collection step to include clear controls for selecting data collection intervals, choosing which signals to merge or compare, and option to opt-in for health score reporting impacting business ROI.
Impact
Time-synchronized data flowing into the model increased users confidence that the model was learning from representative device behavior, leading to more stable and actionable insights in production.


Step 3: Training model
Process
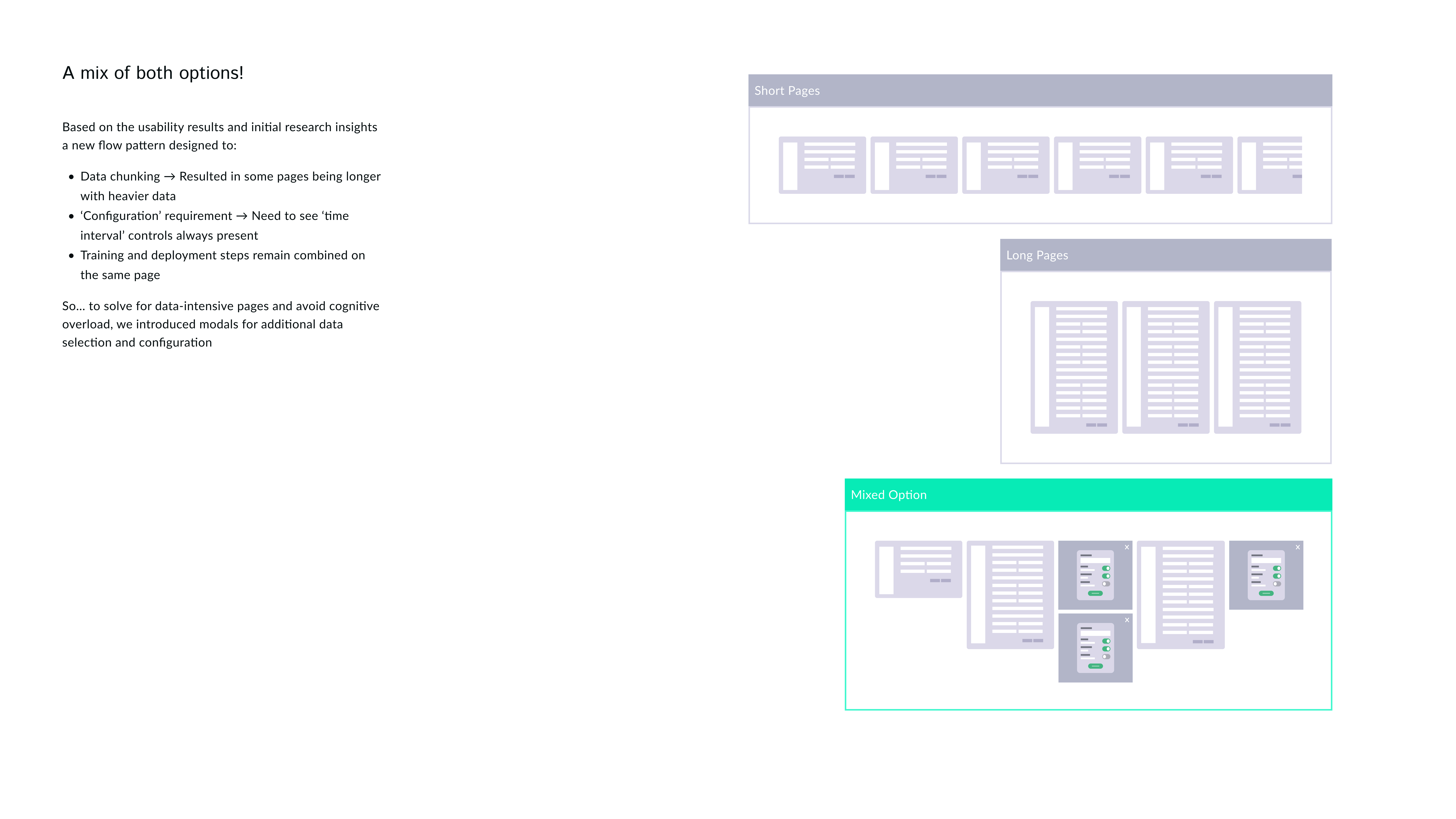
Training and deployment go hand-in-hand, similar workflows combine the two steps into one. We strategically decided to break it down into two separate steps to keep the workflow scalable for feature addition and branching in future.
Also, this helped lift some cognitive load for less technical users giving them more confidence about the tasks they need to perform at each step without overwhelming them.
Training model steps:
1. Set up/define events
2. Run training
3. Monitoring training
03 - Setup & Run Training
Need: Setup & observe training progress
Users needed a straightforward way to provide training data for the model, but data often came from different systems, formats, and time ranges.
Action
Designed a quick way for users to create a new training model and upload custom data for the training.
Impact
This reduced setup errors and rework, ensuring models started from clean, compatible data inputs.

03 - Event Setup
Need: Define training parameters
Users needed a clear way to define which events the model should flag, how critical each condition is, and how long the system should observe behavior before triggering alerts. Without this, models produce noisy or premature alerts, causing alert fatigue.
Action
Introduced a setup panel where users specify threshold conditions, assign severity levels, and set a stabilization period to prevent early false positives during model warm-up.
Impact
This improved alert relevance, allowing the model to mature before influencing operational workflows. Users gained confidence that alerts reflect meaningful and stable deviations.

Reflection
Step 4: Deploy model to node(s)
Process
This step is specific to IoT Edge, where models should be deployed to nodes. I designed batch deployment and undeployment to nodes for faster task completion and provide extra control based on the needs we heard from users.
Deployment tasks:
1. Model deployment (nodes)
2. Model troubleshoot & undeploy (nodes)
3. Monitoring deployment status
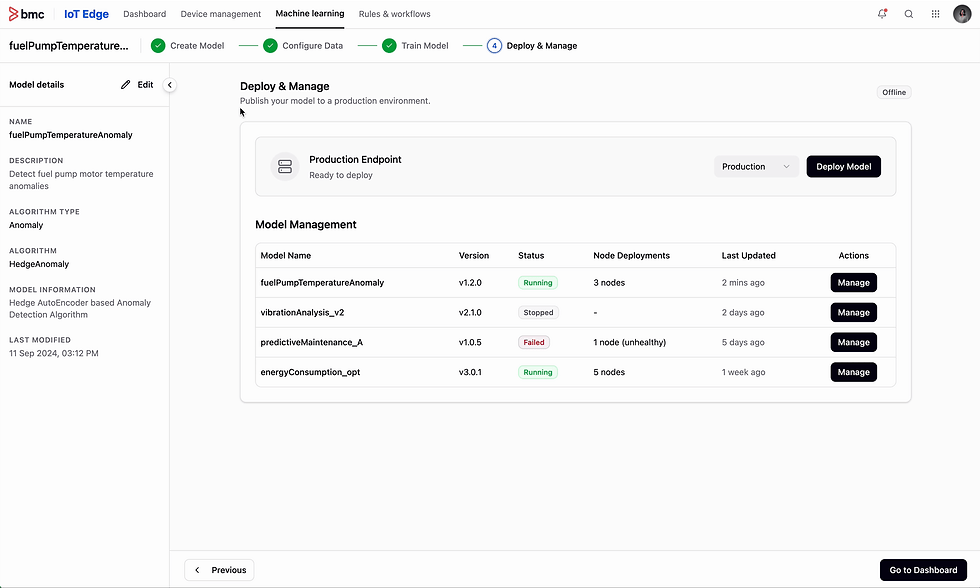
04 - Deploy model
Need: Clear path to deploy models
Users need a clear and reliable way to deploy model into production environments. The process must show live metrics including, latency, error rate and uptime. It should indicate deployment errors and failures for previous deployments.
Action
The interface includes environment selection, and real-time metrics for monitoring.
Impact
This made deployment accessible to less-technical users, reduced dependency on engineering teams, and decreased deployment time from days to minutes.
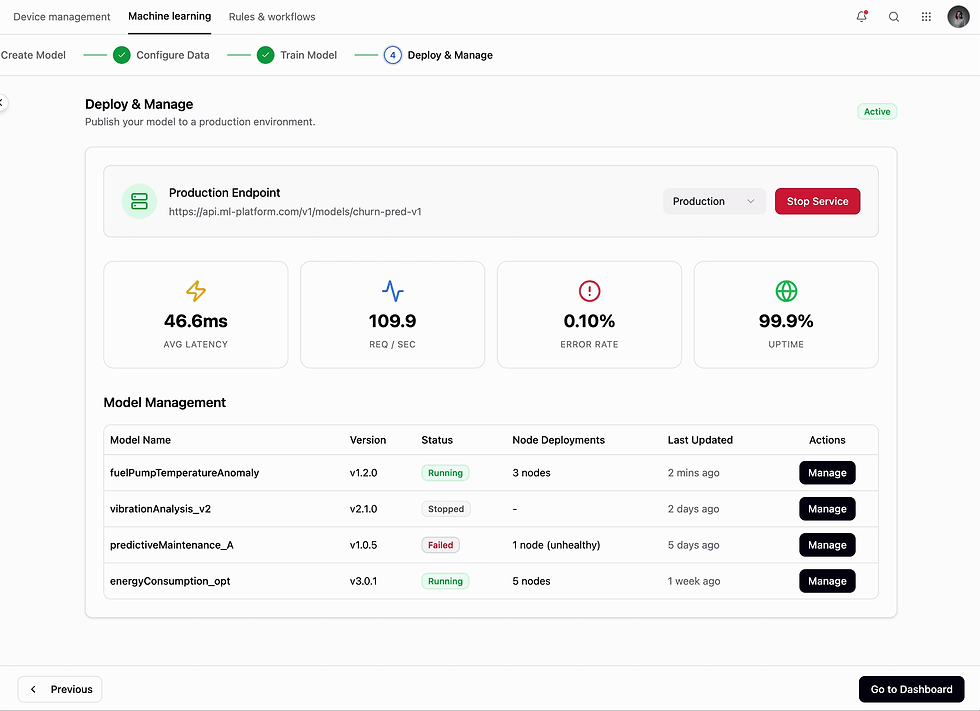
04 - Manage Deployments
Need: Deploy/undeploy to node
Ability to deploy/undeploy a specific model to a node.
Action
Introduced a panel to manage deployment with indications showing which node(s) is causing error.
Impact
This improved operational efficiency for models and surfacing up precisely the nodes that are causing models to fail.
Bridging technical depth with usability
How to translate highly technical MLOps workflows into guided experiences that reduced complexity without oversimplifying critical details
Cross-domain collaboration & design
Gained experience aligning data scientists, ML engineers, and product stakeholders, each with different mental models, around a unified design framework.
Want to see more?
01
Goal
Design an intuitive workflow for technical (and less technical) users to configure, train and deploy ML models within IoT Edge space.
03
Challenge
Should we re-think the entire experience or make incremental improvements? What will give us the biggest user value return on our resource investment?